By Nicholas Brown.
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency based on the increasingly popular blockchain technology. Bitcoin is defined as a cryptocurrency because it utilises cryptography intrinsically to secure users’ funds and verify transactions. The symbol for Bitcoin is BTC.
What’s the point of Bitcoin? Digital cash. It attempts to bring the characteristics of cash to e-commerce. That means: freedom of storage location, freedom to transact any amount, anywhere, at any time of day, and for the lowest possible cost.
Introduction To Bitcoin
A Bitcoin is a form of digital currency which is not a physical coin or a bank-issued note, unlike fiat currencies (conventional currencies) such as the US Dollar, Australian Dollar, or the Chinese Yen. This cryptocurrency is not backed by a tangible item of value such as gold.
However, neither are fiat currencies (conventional currencies such as the USD used to be backed by items of value such as gold, but they no longer are). Bitcoin is also a form of distributed ledger technology (DLT).
Bitcoins are stored in wallets on the blockchain and are divided as easily as conventional currencies, except there is no equivalent term for cents or pennies. If you want to buy something for half a Bitcoin, that equates to 0.5 BTC, and you can simply enter a transaction amount of 0.5 BTC.
Further reading: How to Create A Bitcoin Wallet
Remembering a price like 0.01342 BTC is something you have to get used to, you can use smaller units such as mBTC instead. You can divide it further for transactions without even numbers such as 0.3214 BTC as well, and you won’t have to worry about finding change! (one of the benefits of transferring funds digitally, which, to be fair, benefits fiat currencies as well).
On the blockchain, the smallest unit of a Bitcoin is 1 Satoshi (0.00000001 BTC). 1 BTC = 100,000,000 Satoshi (named after Satoshi Nakamoto).
Who Created Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created by a person that goes by the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin’s source code is currently maintained by the Bitcoin Core developer team. No one owns the network, but nodes may opt to upgrade to the latest versions of Bitcoin released by the Core team.
The Philosophy Behind Bitcoin
A key philosophy behind Bitcoin is fairness. Bitcoin does not (and cannot, unless using a custodian wallet):
- Shut down the accounts of users for any reason, including political dissent, protest, or activism.
- Freeze the accounts of marginalised groups or activists.
- Block users transactions.
- Exclude marginalised groups from accessing its service.
We are living in a time when all of the above are being abused via conventional financial services, and this occurs in numerous countries. Financial censorship is a pillar of oppression because oppressive regimes can (and do) simply freeze the funds of dissidents and marginalised groups.
Misc. Details
| Date Released: | January 9, 2009 |
| Consensus Algorithm | Proof-Of-Work (PoW) |
| Hash Algorithm | SHA-256 |
| Language | C++ |
| Node Software | Bitcoin Core/Bitcoin Daemon |
| Supported OS (for Bitcoin Core node) | Linux, Windows, MacOS |
| Blocks Generated Every | 10 Minutes |
| Block Explorer | Blockchain.info |
| Limited Supply | Yes: 21 Million BTC |
| GitHub | Bitcoin |
| Website | Bitcoin.org |
How Much Is A Bitcoin Worth?
The value of a Bitcoin/the Bitcoin exchange rate is determined by supply and demand. Increased demand drives up the price of Bitcoins, considering that it is not an inflationary currency. There is also an energy cost associated with mining these coins, so they aren’t just paper whimsically churned out of a printing press like conventional money. This deters the inflationary practice of dumping excessive amounts of coins into circulation.
Like fiat currencies, Bitcoins have no intrinsic value. Two former mediums of exchange with intrinsic value are gold and salt. These had intrinsic value because they were useful, regardless of demand or whether they are being traded. People need salt for a variety of purposes such as seasoning, fermentation, and industrial processes, and gold is needed to manufacture electronics, jewellery, among other things.
BTC and dollars are just tokens and notes (respectively). The barter system had one key characteristic over fiat currencies (and cryptocurrencies), and it was that the value of an item was determined primarily by peoples’ wants and needs. Bitcoin is the mother of cryptocurrencies, as it has inspired the invention of technologies such as Ethereum, which has led to the creation of many innovative cryptocurrencies via its platform.
Convert BTC To USDT With An Exchange Rate Calculator
What Can You Do With Bitcoins?
You can use them to purchase items at stores that accept it as a form of payment. You can also purchase them and hold onto them for now, or while the price of that cryptocurrency continues its upward trend. You can buy or sell Bitcoins on cryptocurrency exchanges at any time.
Users that confide in this cryptocurrency often use it as a store of value, unlike many other cryptocurrencies which may be faster and cheaper mediums of exchange. Despite that, Bitcoin fees are still low compared to some fees associated with conventional currencies such as international wire transfers.
Who Accepts Bitcoin As A Payment Method?
Below is a list of some major stores that accept Bitcoin as a payment method, as well as organizations that accept Bitcoin donations.
| Stores And Services That Accept Bitcoin |
|---|
| Overstock |
| ProtonMail |
| Newegg (computer store) |
| Namecheap (web hosting and domain provider) |
| AT&T (Phone and Internet service provider) |
| Whole Foods (retail store chain) |
| ProtonVPN (VPN Service Provider) |
| NordVPN (VPN Service Provider) |
| Private Internet Access (PIA: A VPN Service Provider) |
| Vultr (Cloud Hosting/VPS Provider) |
| Njalla (Cloud Hosting/VPS Provider) |
| Shopify |
| Dish Network |
| Organizations That Accept Bitcoin Donations |
| freeBSD Foundation |
| Free Software Foundation |
| Electronic Frontier Foundation |
| Wikipedia |
How To Purchase Bitcoin
Coins can be obtained by purchasing them from a Bitcoin exchange. Exchanges can be centralized or decentralized. The use of centralized exchanges entails depositing your money into an account you create with them. In some cases, you can store your coins on these exchanges, which carries both benefits and disadvantages from a security standpoint.
A key advantage of a centralized exchange such as Coinbase is their ability to assist you if there is a problem. The reason behind that could also be considered a disadvantage, as they are a prime target for hackers, which can rob you by getting into your Coinbase account.
Please use a hardware or other offline wallet to store your coins instead of Coinbase, Coinspot, and any other service that retains possession of your wallet. Another way to buy Bitcoins is to purchase them from a friend that already has them.
^ Back To The Table Of Contents
The least trivial way to obtain coins is via mining, which requires specialized hardware such as ASIC miners. Mining entails using your computer’s processing power to assist the network with transaction confirmations.
Exchanges That Sell Bitcoin
You can purchase Bitcoins from a number of exchanges including, but not limited to:
- Coinbase (centralized cryptocurrency exchange which allows you to buy cryptocurrencies using USD, as well as sell them in certain countries including the U.S.).
- Coinspot (Australia).
- ShapeShift (decentralized cryptocurrency exchange, and requires you to buy it with another cryptocurrency, not with USD).
- Kraken (centralized Bitcoin exchange).
- Binance (centralized cryptocurrency exchange, and you need another cryptocurrency such as BTC or ETH to buy cryptocurrencies there).
- CEX.io.
Once you have purchased coins from an exchange such as Coinspot or Coinbase, please send them to a trusted offline wallet such as a hardware wallet or a wallet app, specifically one which does not store your private key in an easily-accessible manner.
Trading
Bitcoin can be traded on virtually any cryptocurrency exchange and Bitcoin trading pairs are the most common. What this means is that you can trade Bitcoin for any other cryptocurrency (and very easily).
Difference Between Bitcoin And Conventional Remittance Services
Unlike conventional ‘international’ fiat currency payment services, Bitcoin doesn’t operate by moving physical currency around or using escrow accounts. Bitcoin is a strictly digital currency that can be sent to anyone in the world.
One can buy Bitcoin with their own national currency -> transfer the Bitcoin to a recipient in any other country -> the recipient can sell Bitcoin for their own national currency or keep it if they wish. That concept eliminates the need to move money around, because you are exchanging the money for Bitcoin entirely.
^ Back To The Table Of Contents
How Bitcoin Works
How Bitcoins Are Stored
Bitcoins are stored in wallets, which are stored on Bitcoin’s blockchain network, which is a distributed network of thousands of nodes that each store a copy of Bitcoin’s blockchain. Each of which contains transaction data. Your wallet is controlled by a cryptographic private key which is used to sign outgoing transactions.
This private key is stored on the computer or phone your wallet app is on and the app should encrypt it for you. To access the key, you would generally go into the settings and search for a ‘export private key‘ or ‘show private key‘ option. In some cases it may in be a ‘wallet.dat‘ file on your computer (for example: Bitcoin Core). This is only needed if you are switching to a different wallet app or making a backup copy of your key (which you must always do to avoid losing your funds).
To recover a wallet from a backup, you would look for an ‘import wallet’ option in your new wallet app that allows you to enter your private key or import the ‘wallet.dat’ file. The process is the same if you’ve been gifted a Bitcoin wallet and want to access it.
This is not the digital equivalent of storing your money in a wallet. How it works is, your wallet is used to separate your transactions from everyone else’s. An example of a Bitcoin wallet is an app such as Exodus Wallet, which connects you to the Bitcoin network and makes it easy to initiate transactions.
Exchanges (for example: Coinbase and Coinspot) do not (and cannot) store your coins. They do, however, own and issue wallets (which are stored on the blockchain network like all others).
They provide customers access to those wallets via a username and password (and this is a security vulnerability, because someone just needs to guess your password to access your coins, and of course, your private key and password are stored online on the exchanges’ servers).
What this means, is if someone offers you a hardware wallet or paper wallet, it provides you with access to a wallet on the blockchain. That is not the actual wallet. Paper wallets contain a key pair (your private key, which provides access to your wallet, and your public key, which is your wallet address).
This is why exchanges differ substantially from banks, and should not be treated as banks. Banks serve the purpose of safely storing physical currency.
What Is A Bitcoin Wallet?
A Bitcoin wallet is a pair of cryptographic keys called a private key and a public key. Associated with the public key is all of your transactions. The transactions are stored on a decentralized public ledger (the blockchain), from which your balance is calculated.
This is why one does not simply edit a balance, because there isn’t a balance stored in your wallet. Instead, your wallet app calculates the amount of Bitcoins you can spend based on inbound and outbound transactions. Your public key is your BTC address, which people can send Bitcoins to.
Your wallet’s private key provides access to your funds. Never store your private key anywhere that it can be found. Don’t store it on USB drives that you use for other transfers. It should be stored on a drive which is never used. If you lose your login information, you’re going to need that key to recover your coins. The same applies to your recovery phrase. Never send it or your private key to anyone.
Purchase a drive exclusively for your cryptocurrency wallets and stow it away in a secure place. Never give anyone your recovery phrase, which can be used to gain access to your funds (equivalent to your private key).
If a wallet provider asks you for your private key or recovery phrase, it is a scammer and they are trying to steal your funds.
Find Bitcoin Wallets
Finding a Bitcoin wallet requires a great deal of care due to the fraudulent wallet apps out there that will steal your private key or steal your coins. This is one of the greatest threats you face, therefore you need to use only wallets that are widely known and trusted, and get them only from the original manufacturer or wallet app provider’s website. For app stores, carefully examine all the details of the listings, especially the section underlined in yellow at the bottom-left:

Common Bitcoin wallets include: Ledger Nano (hardware wallet), Trezor (hardware wallet), BitBox (hardware wallet), Bitcoin Core (official desktop/laptop Bitcoin wallet provided by the Bitcoin Foundation), Bitcoin Wallet (Android, and if you’re on iOS you can use BRD), Bitcoin Knots (desktop). Beware of counterfeit wallets pretending to be the ones shown above and look over the reviews and ratings in the app store before you download (this can help to reveal if it is a counterfeit in some cases).
Please bear in mind that wallet apps that run on your phone or computer are susceptible to malware.
A Few Security Tips: Secure Your Bitcoin
Don’t use an exchange to store all your coins. After buying them on an exchange such as Coinbase or Coinspot, send them to an offline wallet. Always look up reviews and ask around before trying an offline wallet. Not all are legitimate.
Never give anyone your wallet's private key! There is never a good reason to do so. Giving someone your private key also gives them your wallet. In order to receive funds, you only need to provide your public key.
Also, don’t buy hardware wallets off Ebay. There are too many fakes there (which will steal your coins). Hardware wallets are actually among the most secure, and you should buy them directly from the manufacturer.
When visiting a website that offers a wallet, or an exchange. Always check the URL in your address bar to ensure it is correct. If you aren’t sure, do a Google search and take a look at all the results, and do your best to ensure it is authentic. There are phishers with fake websites that mimic known exchanges with slightly different URLs.
Also check for SSL and extended validation (or EV, often denoted by a green COMPANY NAME LLC (US) in your browser’s address bar. A green padlock (which is necessary for exchanges, so don’t use any exchange if their website doesn’t have it) in your browser’s address bar indicates that the website you’re visiting has SSL, which encrypts your connection and helps to protect your login credentials from theft.
Go to Binance, Coinbase, and Coinspot, and you’ll see that they all use SSL (denoted by the green padlock mentioned).
Coinbase has extended validation, denoted by Coinbase, Inc. (US) on the left side of your address bar if you use Firefox or Chrome. If you’re visiting the Exodus Wallet website, you’ll see ‘Exodus Movement Inc (US). If you don’t see that, you’re not on the Exodus or Coinbase website. I haven’t seen EV on the Coinspot or Binance website, though, as they don’t appear to have EV.
You may not see an extended validation certificate on every decent website, as it can be expensive, but they must all at least have the green padlock I mentioned above (SSL) to encrypt your credentials before transmitting them to the server.
Malware, Keyloggers, And Other Threats
There are various online threats that could steal your Bitcoin such as keyloggers (these may intercept your password as you type it into an online custodian service or exchange and then login to steal your funds later). Generally, you want to avoid websites that you aren’t sure are trustworthy (whether or not they are cryptocurrency-related) to avoid malware and spyware.
One of the most important things to remember about scammers is that they often try to get you to hand over your private key or recovery phrase, as someone attempted on me, so I made an infographic out of it:
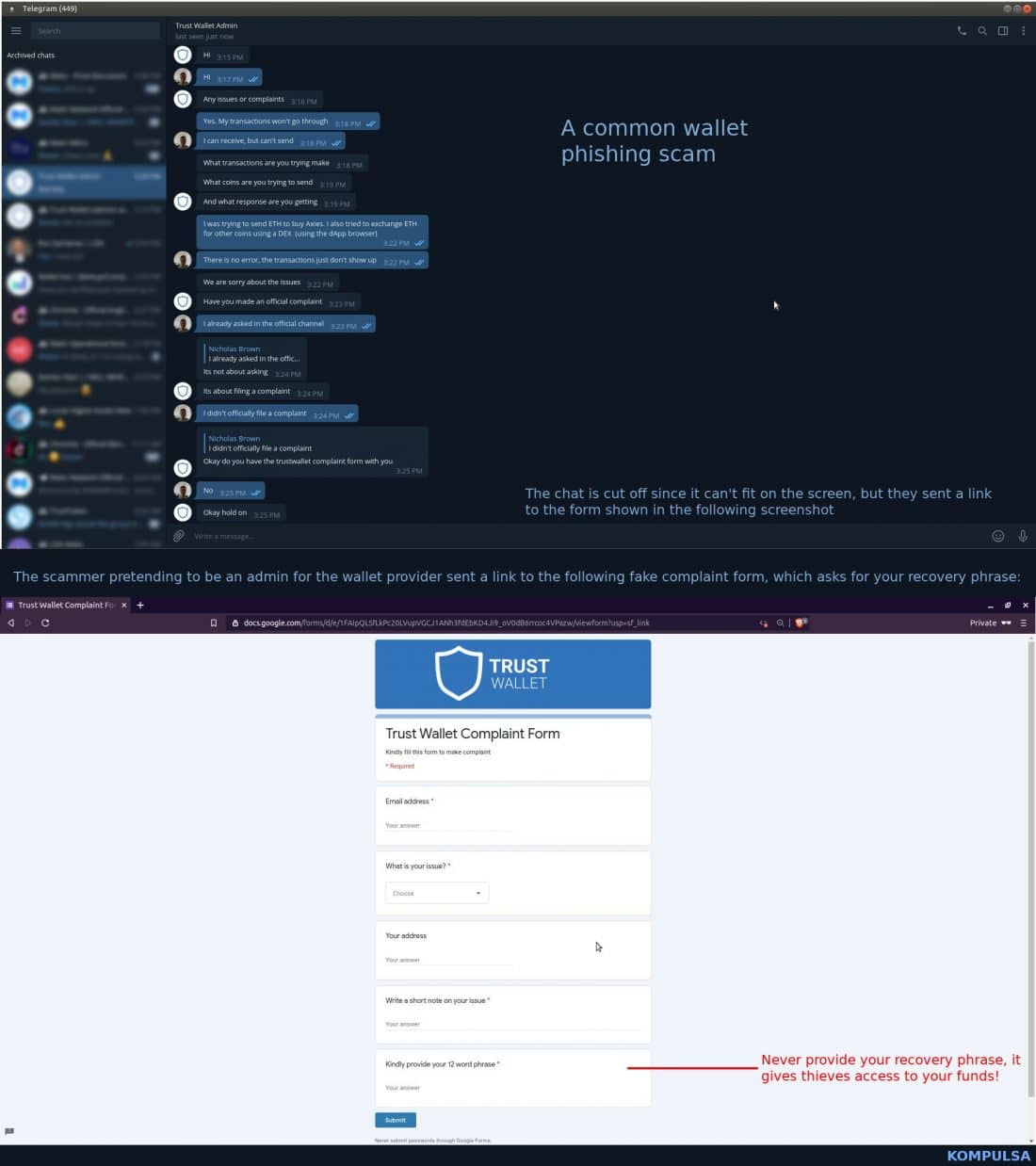
^ Back To The Table Of Contents
How Bitcoin Transactions Work
A Bitcoin transaction is a wallet-to-wallet transaction (the transfer of wealth from one Bitcoin wallet to another). If someone sends 0.5 BTC to your wallet address, your wallet app (or the exchange that holds it) will recalculate how much you own and that 0.5 BTC will be added to it.
If you were to send someone Bitcoin, you would enter the amount in a wallet app, copy and paste in the recipient’s wallet address, and then click send.
The wallet will sign the outgoing transaction with your private key (the key to your wallet) and broadcast it to the nodes on the Bitcoin network. A minimum number of nodes has to verify the validity of the transaction by:
- Ensuring that your wallet has sufficient funds to send.
- Confirming that you are the one that attempted to transfer the funds. This is why you must sign transactions with your private key (thankfully done automatically by your wallet app).
- Verifying the data integrity of the broadcast (ensure there are no errors or tampering with the help of hashing and merkle trees). Tampering with block content will cause hash inconsistencies and break the chain. The result is other nodes on the network will reject the resulting broken part of the chain.
The block containing your transaction must then be mined on the network. Miners receive a fee for the transaction, and currently receive block rewards as well.
Further reading: Bitcoin protocol rules.
Other Notes:
All Bitcoin nodes (full nodes, specifically) contain a copy of a ledger (the blockchain) containing absolutely all Bitcoin transactions. This gives nodes the ability (and responsibility) to verify the hashes of all blocks, and all transactions are stored in blocks.
Mining secures the Bitcoin network. This is partly due to the fact that mining fees entail paying for transactions, so trying to steal Bitcoins could end up costing you in the form of Bitcoin mining fees.
Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. If you accidentally send someone Bitcoin, you will have to ask them to initiate a new transaction valued at that amount in order to get a refund. This isn’t a major problem, but it could be considered a minor inconvenience.
Bitcoin transactions are usually much cheaper than wire transfers for small amounts, and also cheaper than PayPal transfers for larger amounts.
Bitcoin transactions are initiated (and will show up in your wallet) in a matter of seconds, and they are confirmed/completed in an average time of 10 minutes. Network delays, however, can increase this time to minutes, or even hours in extreme cases.
In the event of a financial dispute, the ability to trace Bitcoin transactions on the blockchain could be useful.
Anonymity: Is Bitcoin Anonymous?
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency which uses a publicly-viewable distributed ledger containing all transactions ever made on the network. This is a common characteristic of distributed ledger technology (DLT), and it means that your Bitcoin transactions are viewable and traceable. However, your name and contact information are not attached to your wallet — provided that you use a desktop or other wallet that is not an exchange or custodian service.
You won’t have privacy and can be traced more easily if you:
- Send Bitcoin from your exchange wallet to an external wallet, it can be traced back to you.
- Give people your wallet address so they can send you coins and then reuse that same wallet address for everything else — you can be easily traced.
- Keep receiving coins from various people with the same address. People will be able to see your full wallet balance and will know how much money you have.
- Use an exchange to send, receive, or store your coins.
Most Bitcoin wallets generate a new address whenever you click the receive or request payment button so that your funds aren’t all at the same address. This helps to not only improve the security of your wallet but it helps you to avoid the safety issue of criminals stalking your wallet and robbing you. Avoid using wallets without this feature.
Censorship Resistance: Can Bitcoin Transactions Be Blocked?
Under normal circumstances, no one can block Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin is designed to prevent outside interference with users’ transactions and funds. There is no central authority operating the Bitcoin network (just developers maintaining its source code and publishing new builds that nodes and miners can optionally install).
Nodes and miners would have to agree if they wanted to reverse a recent transaction — and that is an unlikely scenario. All subsequent transactions would also have to be deleted to avoid breaking the blockchain. This is because there are thousands of nodes and miners across the world. An important factor to Bitcoin’s censorship-resistance is the fact that it is immutable. Immutability prevents the deletion of transactions from its network.
Bitcoin’s censorship-resistance is eliminated if you use an exchange or custodian service to store your coins. Storing your Bitcoins on an exchange entails sending your coins to the exchange, which may put you at risk of having your coins stolen or your transactions blocked. Just like how you wouldn’t deposit cash to a bank that you don’t trust, apply the same logic to an exchange.
Network Performance And Efficiency
I can’t say much about the performance and efficiency of the Bitcoin network due to the ongoing variation of hash power available on the network, as well as the backlogs caused by usage spikes (caused by people that hysterically buy or sell their coins due to their fears).
However, the Bitcoin network supports 7 transactions per second. This is due to a block size limitation implemented for security purposes. In 2010, a 1MB block size was imposed, and block size increases have been proposed since then. Increasing block size would also increase the hardware requisites for mining.
As it stands now, a single ASIC miner can easily set you back $6,000 USD. If those get more expensive due to an increased block size, that may result in a more centralized network owned by large businesses, due to a higher financial barrier to entry for prospective miners.
Newer cryptocurrencies inspired both by Bitcoin’s technologies and weaknesses have improved on this with the ability to handle up to thousands of transactions per second. For example, the Ethereum network is capable of 15 transactions per second (this may increase with upcoming upgrades), and Nano (formerly Raiblocks) is capable of an estimated 7,000 transactions per second.
A key characteristic that separates Raiblocks from Ethereum and Bitcoin is that it is minerless. Although mining has solid benefits, it is hampered by these performance limitations, and it is energy-intensive.
Scaling: A Lack Of Scalability Impedes Bitcoin’s Network Throughput
Blockchain scaling is a hot topic, considering Bitcoin’s recent boom in transactions (due to increased popularity and sudden exposure in the mainstream media). Bitcoin is a blockchain implementation that utilizes mining, therefore it can’t process many transactions per second — At least, not on its own!
Layer 2 scaling solutions such as the Lightning Network have been proposed to increase Bitcoin’s transaction capacity from 7 tps (transactions per second) to millions of transactions per second with the help of state channels and smart contracts.
State channels use a smart contract to lock tokens on Bitcoin’s blockchain and establish a two-way connection between the transacting parties so that they can execute their transaction and then write the necessary state update to Bitcoin’s blockchain afterwards. Yes, Bitcoin smart contracts are a real thing!
It is called a layer 2 scaling solution because it does not entail altering Bitcoin’s own consensus algorithm or how Bitcoin’s own chain works (at least not much). Layer 2 blockchain scaling solutions run on top of the blockchain they are helping to scale. Users of the Lightning Network (or those providing wallet services) run Lightning nodes.
Other layer 2 scaling solutions have been proposed, such as side chains. Such a solution entails establishing another blockchain with its own consensus algorithm (something faster than mining such as proof-of-stake) that locks tokens on the main blockchain and conducts transactions on the (significantly faster) side chain.
While layer 2 scaling solutions sound promising, not everyone is a fan. Many varieties of layer 2 scaling solutions use a variant of proof-of-stake consensus algorithms. Some Bitcoin alternatives (for example: EOS) already use that algorithm for their main chain instead of creating a second chain. They, like layer-2 solutions achieve little or no transaction fees.
Security: How Bitcoins Are Mined
What Is Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process whereby complex cryptographic puzzles are solved using nodes (miners, in this case) on the Bitcoin network. Miners essentially contribute their mining rigs’ (specialized computers) processing power to help secure the Bitcoin network and verify transactions for everyone else. Miners are then rewarded with Bitcoins.
This is called a Proof-of-Work system. Many other cryptocurrencies are mined. However, some may transition to a Proof-of-Stake system due to the high cost of mining.
Bitcoin mining used to be profitable with the use of CPU mining rigs. However, ASIC miners have now superseded them due to significantly higher efficiency. ASIC means Application-specific Integrated Circuit.
Mining has provided many with a way to generate an income without spending money on a tertiary education. Some miners join Bitcoin mining pools because they have a higher chance of solving blocks and reaping the reward (coins).
However, the reward is split across the miners across the pool. If you solve a block without joining a mining pool, you have the entire reward to yourself. That’s just harder, unless you have a massive amount of hashpower to increase your chances of solving blocks.
Power Consumption Of Bitcoin Miners
The Volatility Of Bitcoin
The volatility of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is a concern among many, as it causes uncertainty. For some, the upward trend of Bitcoin prices has compensated for that. Fiat currencies around the world have been losing their value to inflation for years, essentially devaluing peoples’ savings and incomes. That makes it harder to get by if wages don’t catch up accordingly.
Bitcoin API: Your Key To Automating Account Management
Bitcoin provides an Application Programming Interface (API) that allows you to programmatically control the Bitcoin Core wallet and monitor Bitcoin transactions, automate Bitcoin transactions, and retrieve various other details about the Bitcoin network and blockchain. You could view the contents of a block, check if a transaction has received enough confirmations, send coins, among many other tasks.
A few examples of such Bitcoin API methods/Bitcoin API commands include:
- getrawtransaction: This will provide the details of a given transaction.
- decoderawtransaction: This decodes the raw transaction data returned by getrawtransaction to make it human-readable.
- getbalance: This will tell you the balance of a given Bitcoin account.
- getinfo: This provides various details about the state of the Bitcoin blockchain.
- getmininginfo, and many others which can be found here.
Here’s an example of an HTTP request being made to the Bitcoin API using Node.js:
var http = require('http'); var options = { host: '127.0.0.1', port: 8332, method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'Basic [password]'} }; function getRawTransaction(txid) { function OnResponse(response) { var data = ''; response.on('data', function(chunk) { data += chunk; //Append each chunk of transaction data received to the 'data' variable }); response.on('end', function() { data = JSON.parse(data); //Parse the complete JSON data received from the Bitcoin API. console.log(data.result); //Print the received transaction data to the terminal to test our code. }); } var request = http.request(options, OnResponse); //Below you tell the API what you are doing using the 'method' field. request.write('{"jsonrpc":"1.0","id":"rpc","method":"getrawtransaction", "params":["' + txid + '"]}'); request.end(); }
So simple! You can use that to build an app that tracks the status of your transaction so you’ll know when it is complete. You can access this API by simply installing Bitcoin Core and running it on your computer or server, as it is Bitcoin Core that provides the API. It will download the entire blockchain to your computer, after which you will have instant access to all the data you’d ever need.
^ Back To The Table Of Contents