Definition
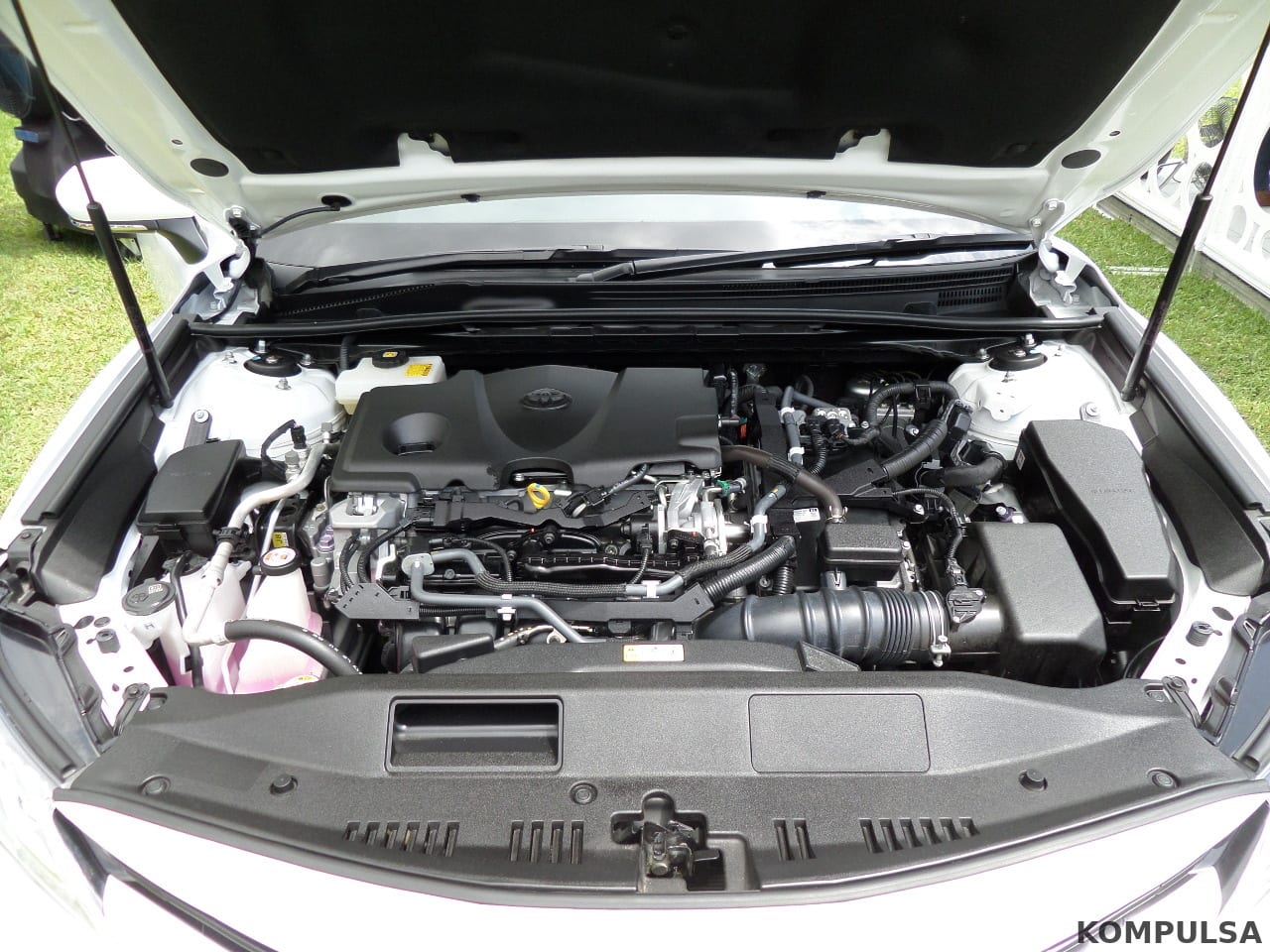
A naturally aspirated engine is defined as an engine that does not utilize forced induction to supply its intake with air. The two most common forms of forced induction in non-naturally aspirated engines is turbocharging and supercharging.
Forced air induction essentially forces additional air into the engine’s cylinders, squeezing more power out of it (and sometimes greater fuel efficiency).
Naturally aspirated engines don’t suffer from ‘turbo lag’, which is a brief delay occurring before the effect of the turbocharger is realized. However, some turbocharged powertrain designs have addressed this delay.
Turbochargers are air compressors driven by the flow of exhaust gases through their built-in turbines.
Superchargers on the other hand are air compressors driven by belts, gears, crankshafts, or an electric motor depending on the configuration. Superchargers don’t suffer from turbo lag.